TOPICS
ACCORDING TO THE SYLLABUS 2020-21
Unit I: Computational Thinking and Programming
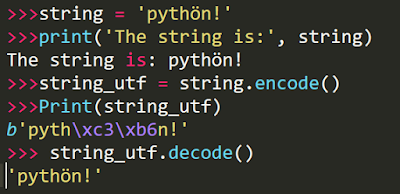
- Revision of basics of Python
- Functions
- File Handling
- Using Python Libraries
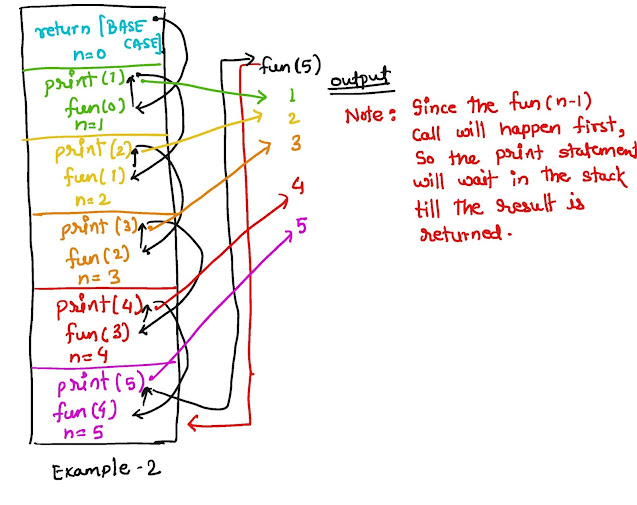
- Recursion
- Idea of Efficiency
- Data-Structures
Unit II: Computer Networks
- Evolution of Networking
- Data Communication Terminologies
- Transmission Media
- Network Devices
- Network Topologies and Types
- Network Protocols
- Mobile Telecommunication Technologies
- Network Security Concepts
- Introduction to Web Services
- E-commerce Payment Transactions
Unit III: Database Management
- Database Concepts
- Relational Data Model
- Structured Query Language (Data Types, SQL Commands, SQL Functions, Joins)
- Interface of Python with SQL Database